Highlits of Planning & Prediction of Self Driving in IROS2020
Robotics ·I have attended IROS2020 mainly focusing on planning and prediction problem in robotics, especially in self driving domain. I would like to share some interesting papers and talks here.
Behavior Planning
Learning hierarchical behavior and motion planning for autonomous driving
Learning behavior decision with occupancy map input and explicit info encoded as road state (traffic light, lane graph). It uses trajectory cost in the rewards function to give more dense rewards.
CMetric: A Driving Behavior Measure Using Centrality Functions
Based on short time obervation (trajs) of agents, assign driving attibute (overspeeding, overtaken, lane change, weaving) in real time. Dynamic geometric graph, centrality function as metric. use 1st order, 2 order, extreme point info to infer the specific driving behavior.
Hierarchical Reinforcement Learning Method for Autonomous Vehicle Behavior Planning
Using hierarchical RL to learn behavior&motion. Shows improvement compared with heuristic-based planner.
Thought
In general, the classic sparse reward problem in RL is tackled by dense rewards from trajectory cost. Thus, hierarchical RL gives more guidance during training. And embeding interactions in graph is promising, as some intrinsic properties in graph can be utilized to identify behavior changes.
Prediction
Vehicles
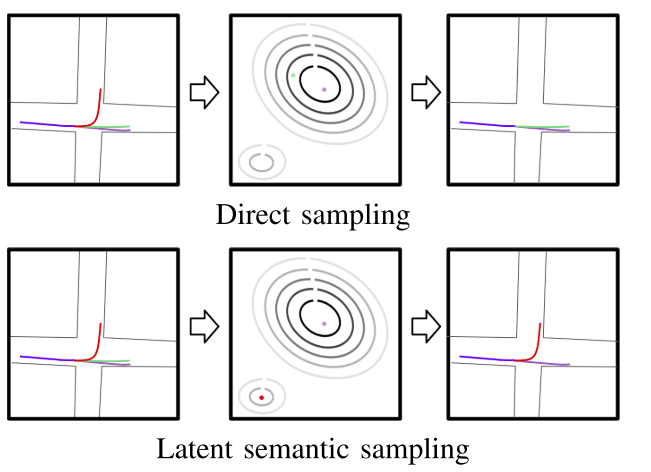
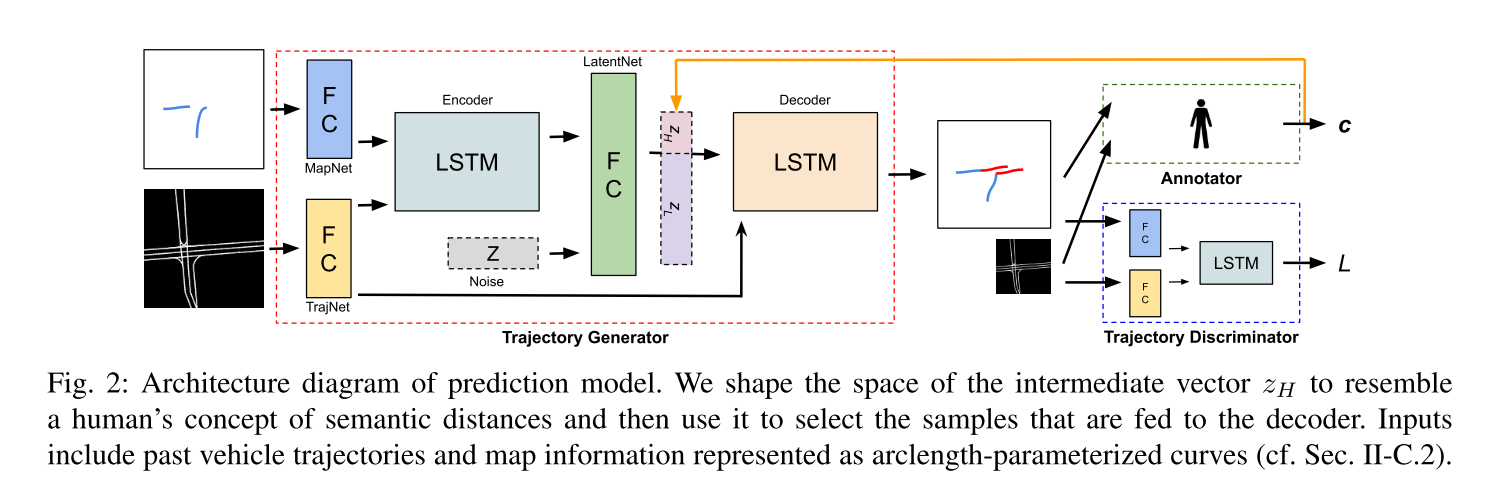
DiversityGAN: Diversity-Aware Vehicle Motion Prediction via Latent Semantic Sampling
This work aims to catch multiple mode of agent’s intents via latent semantic sampling. It uses history trajectories and map as input, and encodes these info to latent space. The latent space is separated in to high level (z_h: maneuver) and low level (z_l: trajectories) space, where the high level space is annotated by humans or classifier. The high level latent space encodes behavior types, e.g. merging, lane keeping, etc. The GAN method is used to train the whole model. When sampling trajectories in latent space, the Farthest Point Sampling (FPS) is used to catch all unique modes.
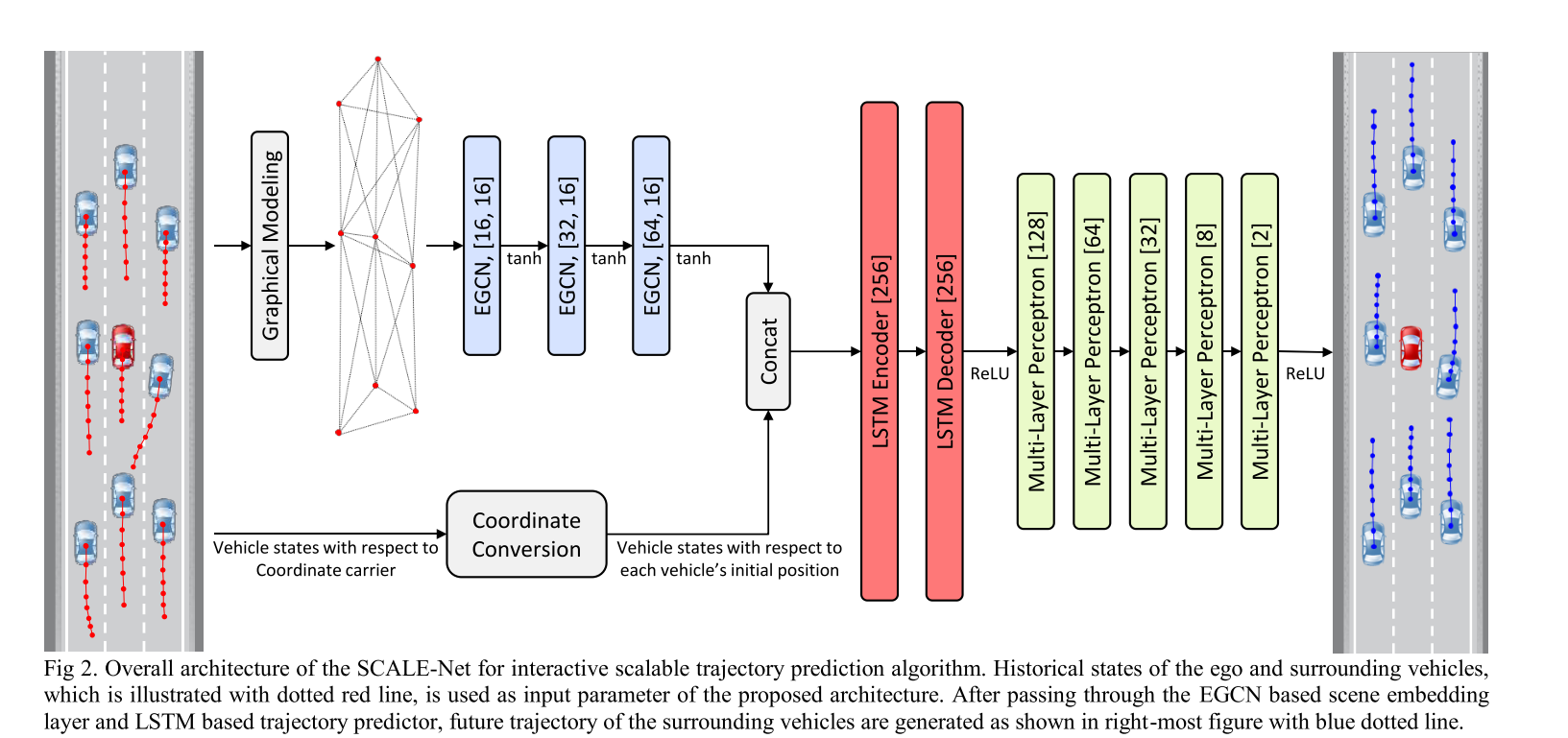
This work aims to have a single short prediction of all agents while considering interactions and real time. The interaction is modeled as Edge Graph Convolution Network. It uses agent’s phisical states(from fusion) to explicitly represent agents. First, attention mechanism is used to assign importance to each agent. Then the agents are simultaneously propogated via the graph convolution with attention importance as weights. The scalability of this approach with random number of agents in scene is much better than CNN-based approach (pixel based). A main drawback is it doesn’t consider map and traffic information (no scene embedding).
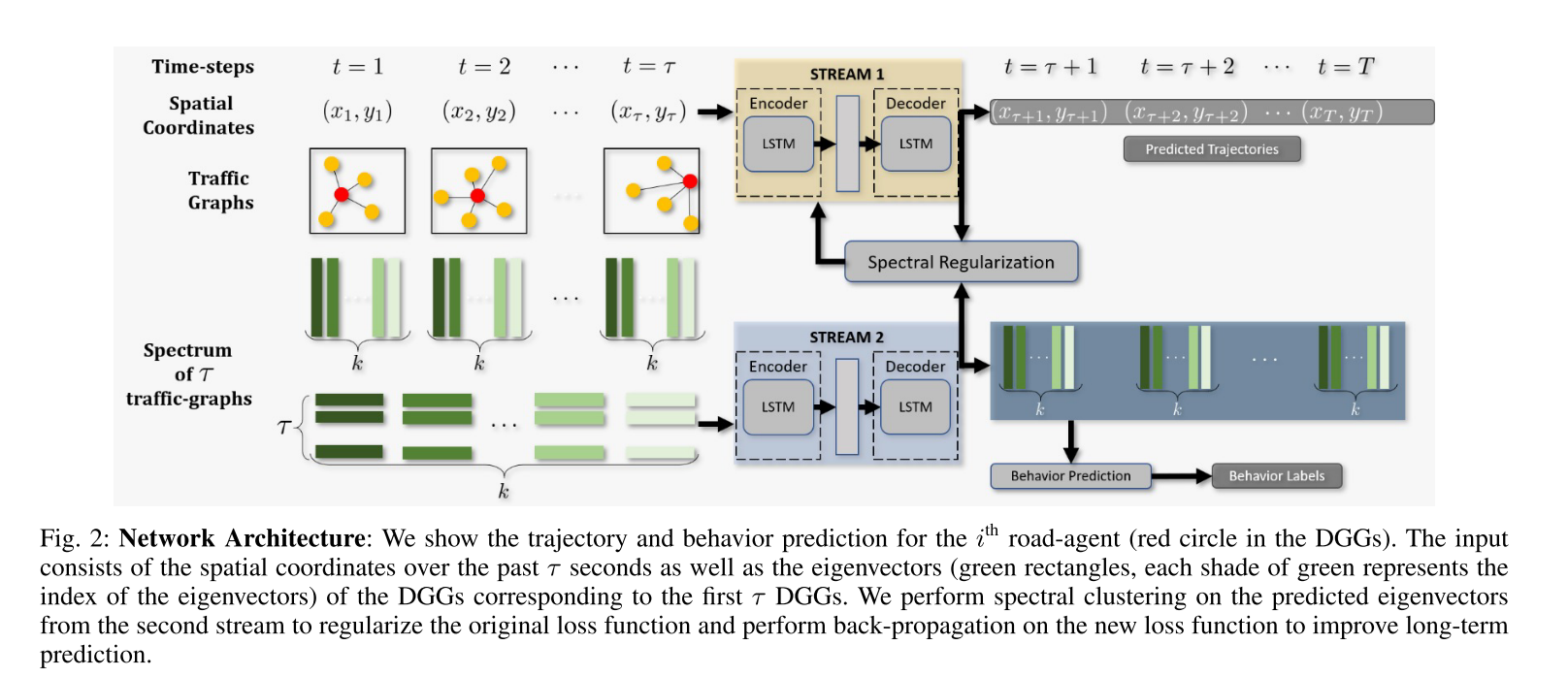
Forecasting Trajectory and Behavior of Road-Agents Using Spectral Clustering in Graph-LSTMs
Predict both behavior type and trajectory using two graph LSTM network. Assuming we have history observations, a dynamic geometric graph (DGN) is build up for each history timestamp to modle interactions among agents. The DGN is purely depends on agent’s position. Based on adjacent matrix of DGN, a Laplacian matrix is derived, and its eigenvetors are reagards as spectrum. These spectrums are fed into one LSTM network to predict behavior types. The behavior prediction result is also fed into another LSTM to regularize the trajectory prediction.
This work tries to learn human driving cost function via demonstrations in a non-deep-learning way. A set of physical features are manually selected:
Non-interaction features:
- speed
- longitudinal & lateral acceleration
- longitudinal jerk
Interactive features:
- future distance: minimal distance of two vehicles in a time window
- future interaction distance: minimal distance from agents to collision point
The partition factor is approximated by efficient sampling method. It uses graph search to find candidate pathes using social force threshold. For each path candidate, the time-optimzed polynomial speed profiles is generated. The learning algorithm converges when feature distribution in samples trajectories are close to human dataset.
Thought
Fast single short trajectory prediction is important for real time project (self driving), besides other requirements like accuracy. The interaction modelling of multiple agents has a trend to use graph neural network. And instead of using anchor methods in Waymo’s paper (MultiPath: Multiple Probabilistic Anchor Trajectory Hypotheses for Behavior Prediction), FPS in latent space is quite promising.